The XRP Ledger (XRPL) currently burns a small amount of XRP per transaction to prevent spam, unlike Ethereum’s EIP-1559, which reduces supply over time. If XRPL implemented a similar fee-burning mechanism, it could potentially burn $44 billion worth of XRP over the next decade, significantly impacting its price.
What to Know:
- The XRP Ledger (XRPL) currently burns a small amount of XRP per transaction to prevent spam, unlike Ethereum’s EIP-1559, which reduces supply over time.
- If XRPL implemented a similar fee-burning mechanism, it could potentially burn $44 billion worth of XRP over the next decade, significantly impacting its price.
- Google Gemini suggests that with massive adoption and utility, XRP’s market cap could reach $5 trillion by 2035, potentially driving the price to around $132.23.
The crypto community is buzzing about the potential impact of implementing a fee-burning mechanism on the XRP Ledger (XRPL), similar to Ethereum’s EIP-1559. Currently, the XRPL burns a negligible amount of XRP per transaction to deter spam, a stark contrast to Ethereum’s approach of reducing token supply. Could a shift towards a deflationary model revolutionize XRP’s value and investor perception?
If the XRPL adopted a fee-burning mechanism akin to Ethereum’s, the network could potentially burn around $4.4 billion worth of XRP annually, totaling $44 billion over the next decade. This would equate to removing approximately 17.187 billion XRP tokens from circulation, potentially driving up the price due to scarcity. The increased activity needed to sustain such burns would also likely attract institutional interest.
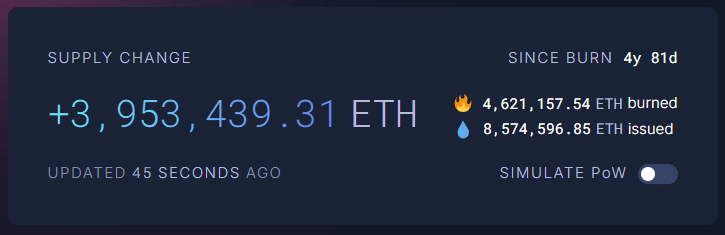
According to Google Gemini, such a change could lead to a bullish scenario where XRP’s market capitalization reaches between $3 trillion and $5 trillion within ten years. This projection assumes massive global adoption and utility of XRP, attracting significant institutional and retail investment. With a reduced supply and increased demand, the value of XRP could see substantial growth.

While the current XRP burn rate is minimal, a strategic shift towards a deflationary model could significantly impact its long-term value and appeal to investors. The potential for a substantial price increase, driven by reduced supply and increased demand, makes this a compelling prospect for the XRP community. However, it’s important to remember that such projections remain speculative and depend heavily on widespread adoption and utility.
Related: XRP Price: $12M Max Pain for Bears
Source: Original article
Quick Summary
The XRP Ledger (XRPL) currently burns a small amount of XRP per transaction to prevent spam, unlike Ethereum’s EIP-1559, which reduces supply over time. If XRPL implemented a similar fee-burning mechanism, it could potentially burn $44 billion worth of XRP over the next decade, significantly impacting its price.
Source
Information sourced from official Ripple publications, institutional research, regulatory documentation and reputable crypto news outlets.
Author
Ripple Van Winkle is a cryptocurrency analyst and founder of XRP Right Now. He has been active in the crypto space for over 8 years and has generated more than 25 million views across YouTube covering XRP daily.
Editorial Note
Opinions are the author's alone and for informational purposes only. This publication does not provide investment advice.


